India’s carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from its power sector fell by 1% year-on-year in the first half of 2025 and by 0.2% over the past 12 months, only the second drop in almost half a century.
As a result, India’s CO2 emissions from fossil fuels and cement grew at their slowest rate in the first half of the year since 2001 – excluding Covid – according to new analysis for Carbon Brief.
The analysis is the first of a regular new series covering India’s CO2 emissions, based on monthly data for fuel use, industrial production and power output, compiled from numerous official sources.
Other key findings on India for the first six months of 2025 include:
- The growth in clean-energy capacity reached a record 25.1 gigawatts (GW), up 69% year-on-year from what had, itself, been a record figure.
- This new clean-energy capacity is expected to generate nearly 50 terawatt hours (TWh) of electricity per year, nearly sufficient to meet the average increase in demand overall.
- Slower economic expansion meant there was zero growth in demand for oil products, a marked fall from annual rates of 6% in 2023 and 4% in 2024.
- Government infrastructure spending helped accelerate CO2 emissions growth from steel and cement production, by 7% and 10%, respectively.
The analysis also shows that emissions from India’s power sector could peak before 2030, if clean-energy capacity and electricity demand grow as expected.
The future of CO2 emissions in India is a key indicator for the world, with the country – the world’s most populous – having contributed nearly two-fifths of the rise in global energy-sector emissions growth since 2019.
In 2024, India was responsible for 8% of global energy-sector CO2 emissions, despite being home to 18% of the world’s population, as its per-capita output is far below the world average.
However, emissions have been growing rapidly, as shown in the figure below.
The country contributed 31% of global energy-sector emissions growth in the decade to 2024, rising to 37% in the past five years, due to a surge in the three-year period from 2021-23.
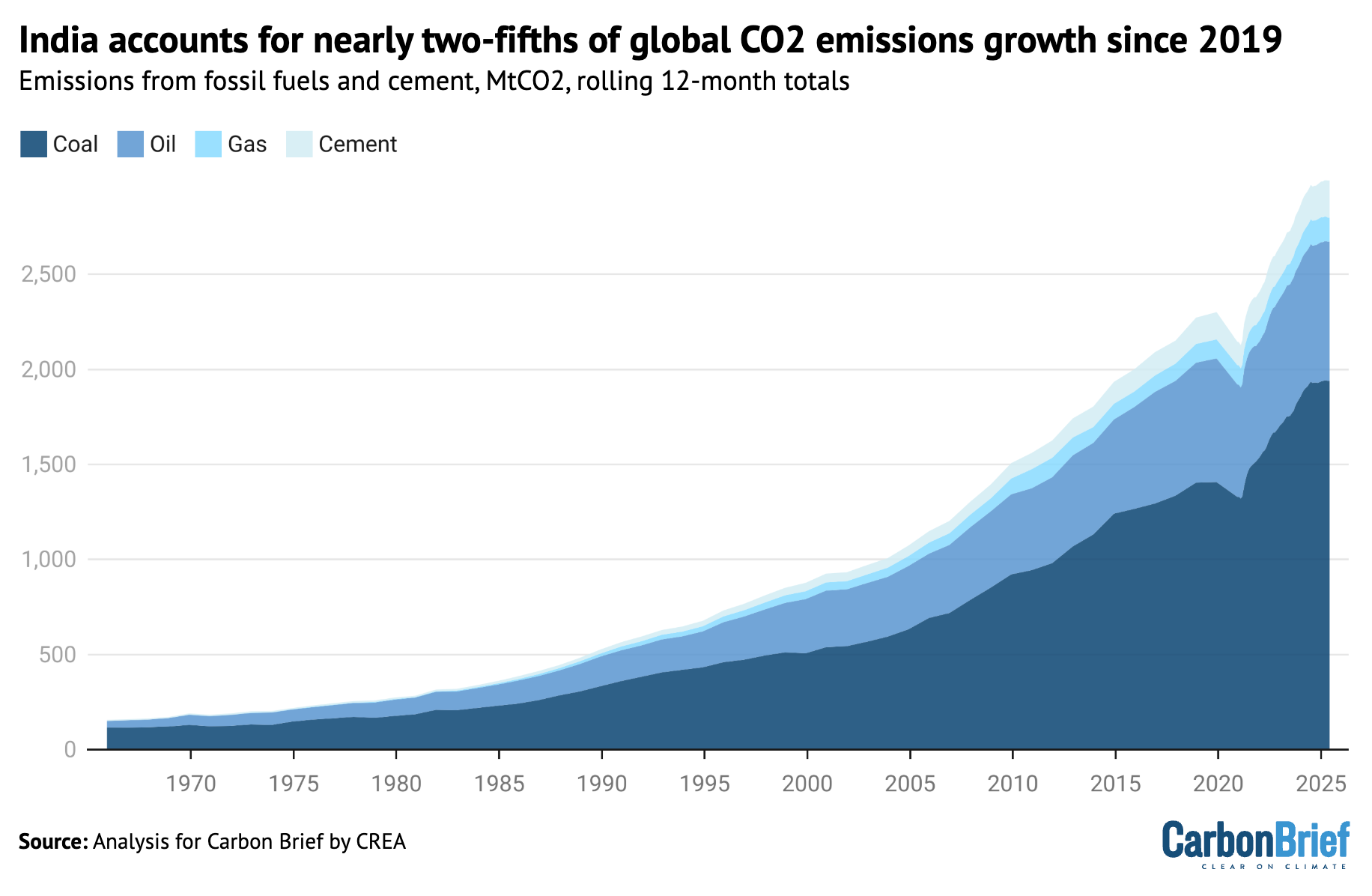
More than half of India’s CO2 output comes from coal used for electricity and heat generation, making this sector the most important by far for the country’s emissions.
The second-largest sector is fossil fuel use in industry, which accounts for another quarter of the total, while oil use for transport makes up a further eighth of India’s emissions.
India’s CO2 emissions from fossil fuels and cement grew by 8% per year from 2019 to 2023, quickly rebounding from a 7% drop in 2020 due to Covid.
Before the Covid pandemic, emissions growth had averaged 4% per year from 2010 to 2019, but emissions in 2023 and 2024 rose above the pre-pandemic trendline.
This was despite a slower average GDP growth rate from 2019 to 2024 than in the preceding decade, indicating that the economy became more energy- and carbon-intensive. (For example, growth in steel and cement outpaced the overall rate of economic growth.)
A turnaround came in the second half of 2024, when emissions only increased by 2% year-on-year, slowing down to 1% in the first half of 2025, as seen in the figure below.
This analysis was written by Anubha Aggarwal, India analyst at CREA; Lauri Myllyvirta, lead analyst at CREA and senior fellow at Asia Society Policy Institute; and Nandikesh Sivalingam, director at CREA.
Read the full analysis here on Carbon Brief.